シンプル・ポジション・コントロール・チュートリアル
このチュートリアルでは、Unityシーン内のダイナミックゲームオブジェクトでInverse3 デバイスのカーソル位置をコントロールする方法を、入門ガイドで紹介したコンセプトに基づいて紹介します。
はじめに
Inverse3 デバイスは2つの制御モードをサポートしている: フォースコントロール そして ポジション・コントロール.
前者がカーソルの位置に基づいて力を調整するのに対し、後者はカーソルの位置を直接操作する。
このチュートリアルでは ダイナミックシーンでのフォースフィードバック チュートリアルを採用している。 CursorSetPosition の中にある。 FixedUpdate メソッドを使って、デバイスのカーソルが動くゲームオブジェクトを追えるようにします。
シーン設定
で説明されているシーンコンフィギュレーションから始めてください。 ダイナミックシーンでのフォースフィードバック チュートリアルを含む。 ハプティック・リグ そして ムービング・ボール によって制御されるゲームオブジェクト。 MovableObject コンポーネントを使用している。
SpherePositionControl コンポーネントの実装
を交換する。 スフィアフォースフィードバック コンポーネントの ムービング・ボール という名前の新しいC#スクリプトでGameObjectを作成する。 SpherePositionControl.cs.
以下のプロパティを SpherePositionControl クラスである:
public Inverse3 inverse3;
public float minSyncDistance = 0.05f;
private bool _isCursorSynchronized;
- inverse3:Inverse3 デバイスコンポーネントへの参照。
- minSyncDistance:カーソルの同期を開始する最小距離のしきい値。
- _isCursorSynchronized:カーソルの動きがムービングボールと同期しているかどうかを示すフラグ。
同期ロジック
ムービングボールへの近接度に基づいてカーソルの同期を開始および停止するメソッドを実装する:
private void StartSynchronizeCursor()
{
var cursorPosition = inverse3.Cursor.transform.position;
GetComponent<MovableObject>().SetTargetPosition(cursorPosition, teleport: true);
_isCursorSynchronized = true;
}
private void StopSynchronizeCursor()
{
_isCursorSynchronized = !inverse3.Release();
}
ここでは
MovableObject.SetTargetPosition(position, teleport:true)をテレポートする。 ムービングボール をカーソル位置に置く。
UpdateメソッドとFixedUpdateメソッド
の中で Update メソッドで、カーソルとカーソルの間の距離に基づいてカーソルの同期を切り替える。 ムービング・ボール:
private void Update()
{
var distance = Vector3.Distance(inverse3.CursorPosition, transform.position);
if (!_isCursorSynchronized && distance <= minSyncDistance)
{
StartSynchronizeCursor();
}
else if (_isCursorSynchronized && distance > minSyncDistance)
{
StopSynchronizeCursor();
}
}
で FixedUpdateカーソルの位置を ムービング・ボール 同期が有効な場合:
private void FixedUpdate()
{
if (_isCursorSynchronized)
{
inverse3.CursorSetPosition(transform.position);
}
}
FixedUpdateメソッドを使用すると、グラフィックのレンダリングパフォーマンスに依存せず、安定したフレームレートで位置制御が動作するようになります。
初期設定
で Awake()を確実にする。 ムービング・ボール は、Inverse3 デバイスがアクセス可能な位置で、そのハンドに関係なくスタートする:
private void Awake()
{
inverse3.DeviceOpened.AddListener(device =>
{
GetComponent<MovableObject>().SetTargetPosition(((Inverse3)device).WorkspaceCenter, teleport: true);
});
}
ゲーム体験
Inverse3 デバイスを固定し、十分なスペースを確保してください。 プレイモードを起動し、カーソルをムービングボールに近づけると、Inverse3 がムービングボールの動きに追従します。 キーボード入力を使ってムービングボールを動かすことができ、カーソルがムービングボールの位置を追跡できることを示す。
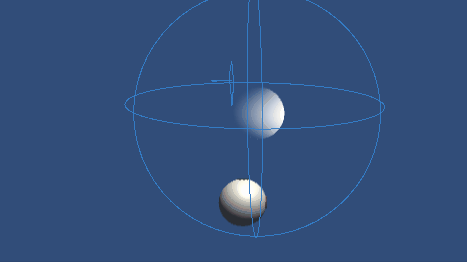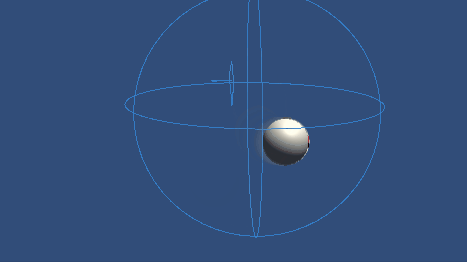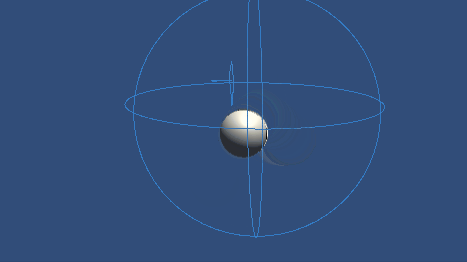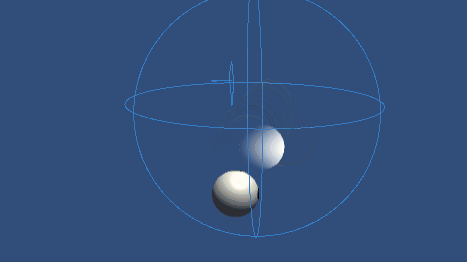
ソースファイル
このチュートリアルの完全なシーンと関連ファイルは チュートリアル サンプルは Unity Package Manager 内にあります。
これには MovableObject スクリプトは、キーボード入力でゲームオブジェクトの動きを制御するために、いくつかの例で利用されています。
スフィアポジションコントロール.cs
/*
* Copyright 2024 Haply Robotics Inc. All rights reserved.
*/
using Haply.Inverse.Unity;
using Haply.Samples.Tutorials.Utils;
using UnityEngine;
namespace Haply.Samples.Tutorials._5_SimplePositionControl
{
/// <summary>
/// Controls the Inverse3 cursor position based on the current position of this GameObject.
/// When the GameObject is within a specified distance from the cursor, it initiates synchronized control,
/// allowing the cursor to follow the GameObject's movements.
/// </summary>
[RequireComponent(typeof(MovableObject))]
public class SpherePositionControl : MonoBehaviour
{
public Inverse3 inverse3;
[Tooltip("Minimum distance required to initiate synchronized control between this GameObject and the Inverse3 cursor.")]
[Range(0, 1)]
public float minSyncDistance = 0.05f;
private bool _isCursorSynchronized;
private void Awake()
{
// Ensure inverse3 is set, finding it in the scene if necessary.
if (inverse3 == null)
{
inverse3 = FindObjectOfType<Inverse3>();
}
// When inverse3 is ready, so the handedness is defined
inverse3.DeviceOpened.AddListener(device =>
{
var inverse3 = (Inverse3)device;
// Teleport the sphere to its workspace center to ensure it can be reached,
// regardless of whether the device is left or right-handed. This ensures the GameObject starts in a
// position that is accessible by the Inverse3 device.
GetComponent<MovableObject>().SetTargetPosition(((Inverse3)device).WorkspaceCenter, teleport:true);
});
}
private void OnDisable()
{
// Ensure movement synchronization is disabled when the component is disabled.
StopSynchronizeCursor();
}
private void Update()
{
// Calculate the distance between the Inverse3 position and this object's position.
var distance = Vector3.Distance(inverse3.CursorPosition, transform.position);
// Enable synchronized movement if within the minimum sync distance and not already synced.
if (!_isCursorSynchronized && distance <= minSyncDistance)
{
StartSynchronizeCursor();
}
// Disable synchronized movement if outside the minimum sync distance and currently synced.
else if (_isCursorSynchronized && distance > minSyncDistance)
{
StopSynchronizeCursor();
}
}
private void FixedUpdate()
{
if (_isCursorSynchronized)
{
// If in sync, set the Inverse3 cursor position to this object's position.
inverse3.CursorSetPosition(transform.position);
}
}
private void StartSynchronizeCursor()
{
// Get the current cursor position.
var cursorPosition = inverse3.Cursor.transform.position;
// Teleport this object to the cursor position to avoid a sudden jump when position control starts.
GetComponent<MovableObject>().SetTargetPosition(cursorPosition, teleport:true);
// Start synchronizing the movement of this object with the cursor.
_isCursorSynchronized = true;
}
private void StopSynchronizeCursor()
{
// Stop synchronizing the movement.
_isCursorSynchronized = !inverse3.Release();
}
}
}