基本的なフォース・フィードバック・チュートリアル
このチュートリアルでは、剛性と減衰の両方を組み込んだ基本的な触覚シミュレーションを作成し、球体のような静的物体との接触の物理的特性をシミュレートします。 このチュートリアルの終わりには、球体の存在を感じ、異なる触覚体験のためにその剛性と減衰特性を調整できるシミュレーションができます。
はじめに
このチュートリアルの核となる課題は、剛性と 減衰の両方を示す球体との接触から生じる力を計算できる関数を開発することです。 この文脈での剛性はバネのような働きをし、圧縮されればされるほど大きな力を発生します。 一方、減衰は物体の動きに対する抵抗を表し、速く動くほど抵抗が大きくなります。
シーン設定
で説明されているように、Haptic Rigをセットアップすることから始めます。 スタートガイドを確保する。 ハプティック・オリジンの位置、回転、スケールが設定される。 (0, 0, 0) そして (1, 1, 1) それぞれだ。
次に Sphere 以下の特性を持つ:
- ポジション
(0, 0, -0.1)(デバイスの前方約10cm) - 規模が大きい:
(0.2, 0.2, 0.2)(直径20cmの球体に相当)
フォース・フィードバック・スクリプト
新しいC#スクリプトを スフィア という名前のGameObject SphereForceFeedback.cs.
このスクリプトは、剛性と減衰の両方を考慮して、球との接触時にInverse3 カーソルにかかる力を計算します。
以下のプロパティでスクリプトを初期化します:
[SerializeField]
private Inverse3 inverse3;
[Range(0, 800)]
public float stiffness = 300f;
[Range(0, 3)]
public float damping = 1f;
private Vector3 _ballPosition;
private float _ballRadius;
private float _cursorRadius;
力の計算は、カーソルが球を貫通したときにのみ発生し、定義された剛性と減衰を持つ物理的な物体に触れた感覚をシミュレートします。
そのため ForceCalculation メソッドがこれを担当し、カーソルの位置と速度の両方を考慮する:
private Vector3 ForceCalculation(Vector3 cursorPosition, Vector3 cursorVelocity, float cursorRadius,
Vector3 otherPosition, float otherRadius)
{
var force = Vector3.zero;
var distanceVector = cursorPosition - otherPosition;
var distance = distanceVector.magnitude;
var penetration = otherRadius + cursorRadius - distance;
if (penetration > 0)
{
// Normalize the distance vector to get the direction of the force
var normal = distanceVector.normalized;
// Calculate the force based on penetration
force = normal * penetration * stiffness;
// Apply damping based on the cursor velocity
force -= cursorVelocity * damping;
}
return force;
}
private void OnDeviceStateChanged(object sender, Inverse3EventArgs args)
{
var inverse3 = args.DeviceController;
// Calculate the ball force
var force = ForceCalculation(inverse3.CursorLocalPosition, inverse3.CursorLocalVelocity,
_cursorRadius, _ballPosition, _ballRadius);
inverse3.SetCursorLocalForce(force);
}
の中で Awake メソッド、初期化 _ballPosition, _ballRadiusそして _cursorRadius でシーンデータを設定する:
private void SaveSceneData()
{
var t = transform;
_ballPosition = t.position;
_ballRadius = t.lossyScale.x / 2f;
_cursorRadius = inverse3.Cursor.Radius;
}
private void Awake()
{
SaveSceneData();
}
の登録と解除を確実に行うこと。 OnDeviceStateChanged コールバック OnEnable そして OnDisable メソッドを使って、相互作用中のフォース・フィードバックを適切に処理している:
protected void OnEnable()
{
inverse3.DeviceStateChanged += OnDeviceStateChanged;
}
protected void OnDisable()
{
inverse3.DeviceStateChanged -= OnDeviceStateChanged;
}
ゲーム体験
Inverse3 カーソルを保持したまま、プレイモードに入り、球体に触れてみてください。 球体の存在を感じ、Unityインスペクタで剛性と減衰のプロパティを操作し、バーチャルオブジェクトとのインタラクションを具体的に感じることができるはずです。
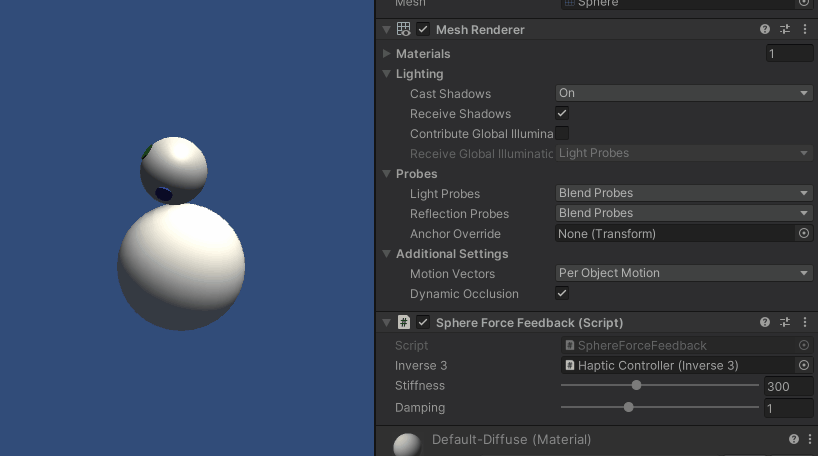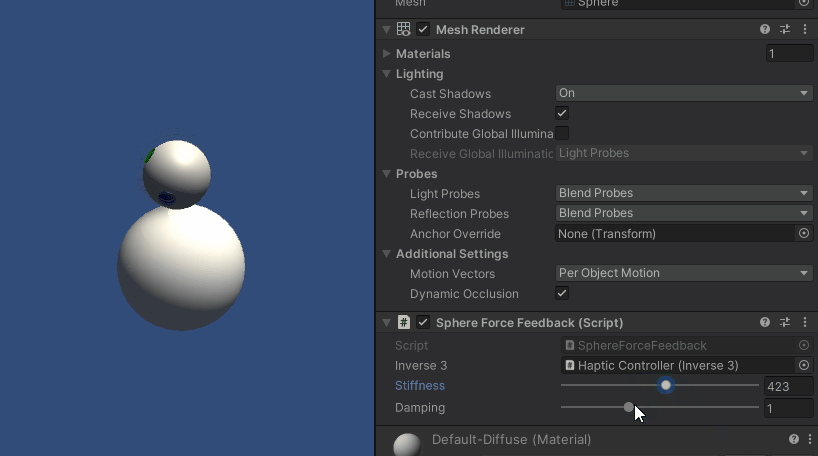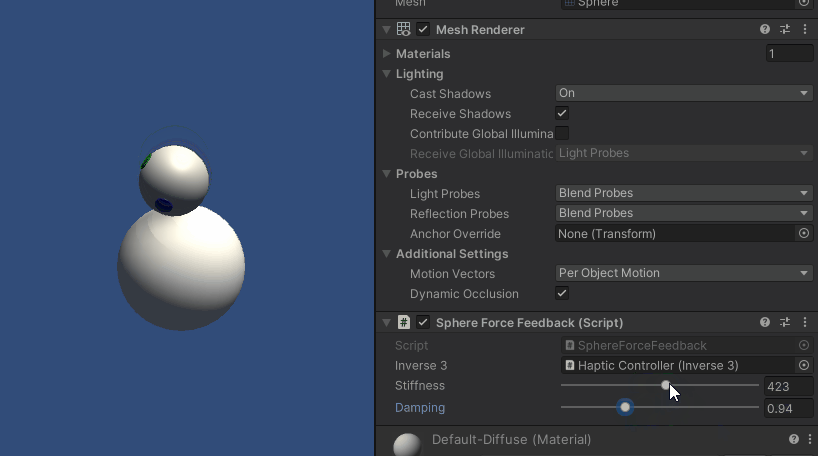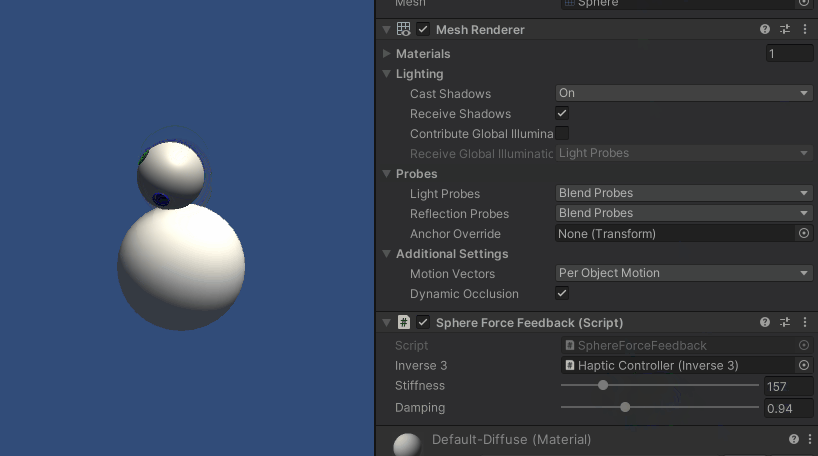
ソースファイル
この例の完全なシーンとすべての関連ファイルは、Unity Package Manager のTutorialsサンプルからインポートできます。
スフィアフォースフィードバック.cs
/*
* Copyright 2024 Haply Robotics Inc. All rights reserved.
*/
using Haply.Inverse.DeviceControllers;
using Haply.Inverse.DeviceData;
using UnityEngine;
namespace Haply.Samples.Tutorials._2_BasicForceFeedback
{
public class SphereForceFeedback : MonoBehaviour
{
public Inverse3Controller inverse3;
[Range(0, 800)]
// Stiffness of the force feedback.
public float stiffness = 300f;
[Range(0, 3)]
public float damping = 1f;
private Vector3 _ballPosition;
private float _ballRadius;
private float _cursorRadius;
/// <summary>
/// Stores the cursor and sphere transform data for access by the haptic thread.
/// </summary>
private void SaveSceneData()
{
var t = transform;
_ballPosition = t.position;
_ballRadius = t.lossyScale.x / 2f;
_cursorRadius = inverse3.Cursor.Radius;
}
/// <summary>
/// Saves the initial scene data cache.
/// </summary>
private void Awake()
{
inverse3 ??= FindObjectOfType<Inverse3Controller>();
inverse3.Ready.AddListener((device, args) => SaveSceneData());
}
/// <summary>
/// Subscribes to the DeviceStateChanged event.
/// </summary>
private void OnEnable()
{
inverse3.DeviceStateChanged += OnDeviceStateChanged;
}
/// <summary>
/// Unsubscribes from the DeviceStateChanged event.
/// </summary>
private void OnDisable()
{
inverse3.DeviceStateChanged -= OnDeviceStateChanged;
inverse3.Release();
}
/// <summary>
/// Calculates the force based on the cursor's position and another sphere position.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="cursorPosition">The position of the cursor.</param>
/// <param name="cursorVelocity">The velocity of the cursor.</param>
/// <param name="cursorRadius">The radius of the cursor.</param>
/// <param name="otherPosition">The position of the other sphere (e.g., ball).</param>
/// <param name="otherRadius">The radius of the other sphere.</param>
/// <returns>The calculated force vector.</returns>
private Vector3 ForceCalculation(Vector3 cursorPosition, Vector3 cursorVelocity, float cursorRadius,
Vector3 otherPosition, float otherRadius)
{
var force = Vector3.zero;
var distanceVector = cursorPosition - otherPosition;
var distance = distanceVector.magnitude;
var penetration = otherRadius + cursorRadius - distance;
if (penetration > 0)
{
// Normalize the distance vector to get the direction of the force
var normal = distanceVector.normalized;
// Calculate the force based on penetration
force = normal * penetration * stiffness;
// Apply damping based on the cursor velocity
force -= cursorVelocity * damping;
}
return force;
}
/// <summary>
/// Event handler that calculates and send the force to the device when the cursor's position changes.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender">The Inverse3 data object.</param>
/// <param name="args">The event arguments containing the device data.</param>
private void OnDeviceStateChanged(object sender, Inverse3EventArgs args)
{
var inverse3 = args.DeviceController;
// Calculate the ball force
var force = ForceCalculation(inverse3.CursorLocalPosition, inverse3.CursorLocalVelocity,
_cursorRadius, _ballPosition, _ballRadius);
inverse3.SetCursorLocalForce(force);
}
}
}