ダイナミックシーンでのフォースフィードバック チュートリアル
基本的なフォースフィードバックのチュートリアルを基に、このガイドではUnity内で動的なインタラクションをシミュレートする方法を紹介し、ユーザーが動いているオブジェクトからフォースフィードバックを感じることができるようにします。 このシナリオは、触覚フィードバックのための高頻度の更新の必要性を強調しており、Unityのビジュアルレンダリングのための一般的な更新レートを大幅に超えています。
はじめに
説得力のある触覚体験、特にダイナミックなシーンでは、1kHz以上の周波数で計算を行うことが極めて重要です。 これは、60Hz前後で動作する通常のゲーム更新ループとは対照的です。 課題は、メインのゲームループと並行してこれらの高周波数更新を管理し、一貫性のある正確なフォースフィードバックを維持するためのスレッドセーフなデータ交換を確保することにあります。
基本的なフォース・フィードバック・セットアップの拡張
のシーンセットアップから始める。 基本的なフォース・フィードバック チュートリアル動的な振る舞いを取り入れるために SphereForceFeedback スクリプトを使用することで、球体の動きに反応し、動的に動くオブジェクトとのインタラクションをシミュレートすることができる。
主な修正点
- ダイナミックなオブジェクトの動き:ユーザー入力または事前に定義された移動パターンに基づいて、スフィアの位置と速度を更新するロジックを組み込みます。
- スレッドセーフなデータ交換:を使用する。
ReaderWriterLockSlimメインスレッドとハプティックスレッド間の共有データへの同時アクセスを管理する。 - フォース計算の調整:を変更する。
SphereForceFeedback.ForceCalculationメソッドを使って球体の速度を考慮し、位置と動きの両方に基づくリアルなフィードバックを提供する。
ダイナミックな交流
動く球体をシミュレートするには、手動で球体の位置を Update メソッドを使うか、キーボード入力やその他のインタラクションに基づいて動きを制御する別のコンポーネントを使う。
この例では スフィア ゲームオブジェクトを ムービング・ボール を追加する。 MovingObject で与えられた チュートリアル サンプル。
調整 ForceCalculation 運動のために
フォースフィードバックの計算はムービングボールの速度を考慮する必要があり、インタラクションの位置と速度の両方に基づいて力を調整します。 これにより、インタラクションのダイナミックな性質を反映し、よりニュアンスに富んだリアルな触覚が得られます。
- 追加
Vector3otherVelocityメソッドパラメータ - 交換
force -= cursorVelocity * dampingによってforce -= (cursorVelocity - otherVelocity) * damping
private Vector3 ForceCalculation(Vector3 cursorPosition, Vector3 cursorVelocity, float cursorRadius,
Vector3 otherPosition, Vector3 otherVelocity, float otherRadius)
{
var force = Vector3.zero;
var distanceVector = cursorPosition - otherPosition;
var distance = distanceVector.magnitude;
var penetration = otherRadius + cursorRadius - distance;
if (penetration > 0)
{
// Normalize the distance vector to get the direction of the force
var normal = distanceVector.normalized;
// Calculate the force based on penetration
force = normal * penetration * stiffness;
// Calculate the relative velocity
var relativeVelocity = cursorVelocity - otherVelocity;
// Apply damping based on the relative velocity
force -= relativeVelocity * damping;
}
return force;
}
スレッドセーフなデータ交換
オブジェクトがリアルタイムで動き、相互作用するダイナミックなシーンでは、同時アクセスによるデータの破損を引き起こすことなく、ハプティックフィードバックの計算が最新のデータに基づいて行われることを保証することが極めて重要です。 そこで、スレッドセーフなデータ交換が不可欠になります。
スレッドセーフなデータ交換のためのキーコンセプト
- スレッドセーフ・メカニズム:利用する
ReaderWriterLockSlimを使用して、同時データアクセスを管理する。これにより、複数回の読み取りまたは1回の書き込み操作が可能になり、データの整合性が確保される。 - データの読み書き:
- 読み取り:ハプティックスレッドは、読み取りロックの下でオブジェクトの位置と速度を読み取り、データの更新を妨げないようにする。
- 書き込み:メイン・スレッドによるオブジェクト・データの更新は、書き込みロックの下で行われ、データ状態の不整合につながる可能性のある同時読み取りや書き込みを防ぐ。
Unityでの実装
-
シーンデータのための構造体:スレッドセーフな操作を容易にするために、シーンに関するすべての必要なデータを保持する構造体を定義する。 この構造体には、ムービングボールとカーソルの位置と速度、そしてそれらの半径が含まれる。 このデータ構造は、スレッドセーフなデータ交換の基礎となる。
private struct SceneData
{
public Vector3 ballPosition;
public Vector3 ballVelocity;
public float ballRadius;
public float cursorRadius;
}
private SceneData _cachedSceneData; -
ロックの初期化:A
ReaderWriterLockSlimインスタンスが初期化され、シーンデータへのアクセスを管理する。 このロックにより、複数のスレッドが同時にデータを読み取ったり、単一のスレッドが書き込むためにデータを排他的にロックしたりすることができ、同時処理中のデータの整合性が保証されます。private ReaderWriterLockSlim _lock = new ReaderWriterLockSlim(); -
書き込みロックによるキャッシュへの書き込み:について
SaveSceneDataメソッドは、書き込みロック内でシーンデータを更新する。 これにより、あるスレッドがデータを更新している間、他のスレッドは読み書きができないので、データの競合を防ぎ、一貫性を確保することができる。private void SaveSceneData()
{
_cacheLock.EnterWriteLock();
try
{
var t = transform;
_cachedSceneData.ballPosition = t.position;
_cachedSceneData.ballRadius = t.lossyScale.x / 2f;
_cachedSceneData.cursorRadius = inverse3.Cursor.Model.transform.lossyScale.x / 2f;
_cachedSceneData.ballVelocity = _movableObject.CursorVelocity;
}
finally
{
_cacheLock.ExitWriteLock();
}
} -
キャッシュからの読み取りロック:について
GetSceneDataメソッドは、読み取りロックの下でシーンデータを取得します。 これにより、複数のスレッドが書き込み操作に干渉することなく安全にデータを同時に読み取ることができ、触覚フィードバックの計算が最新のシーンデータに基づいていることが保証されます。private SceneData GetSceneData()
{
_cacheLock.EnterReadLock();
try
{
return _cachedSceneData;
}
finally
{
_cacheLock.ExitReadLock();
}
} -
メインスレッドデータ更新:について
FixedUpdateメソッドを使用して、メインスレッドでシーンデータを定期的に更新する。 これにより、触覚フィードバックの計算が最新のデータにアクセスできるようになり、シーンの動的な性質を反映します。private void FixedUpdate()
{
SaveSceneData();
} -
更新されたデータによる力計算の適用:での
OnDeviceStateChangedコールバック、力の計算は、スレッドセーフメソッドを通して得られる最新のシーンデータを使って実行されます。これにより、力のフィードバックが正確で、シーン内のダイナミックな相互作用に反応することが保証されます。var sceneData = GetSceneData();
var force = ForceCalculation(device.CursorLocalPosition, device.CursorLocalVelocity, sceneData.cursorRadius,
sceneData.ballPosition, sceneData.ballVelocity, sceneData.ballRadius);
ゲーム体験
これらのスクリプトの強化により、シーン上をアクティブに移動する球体とのインタラクションが可能になりました。 触覚フィードバックは球体の軌跡に動的に適応し、より没入的で触覚的に豊かな体験を提供します。
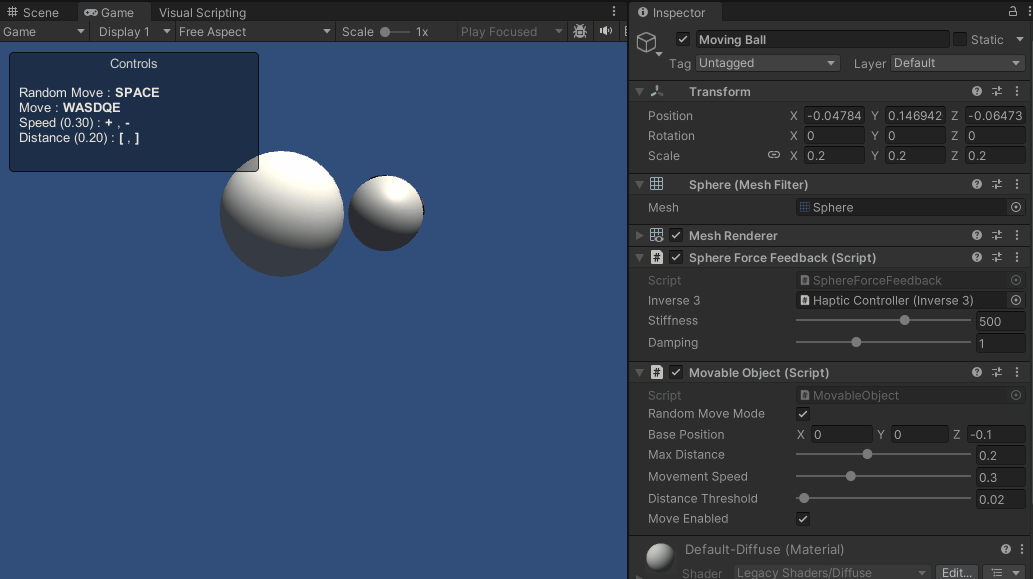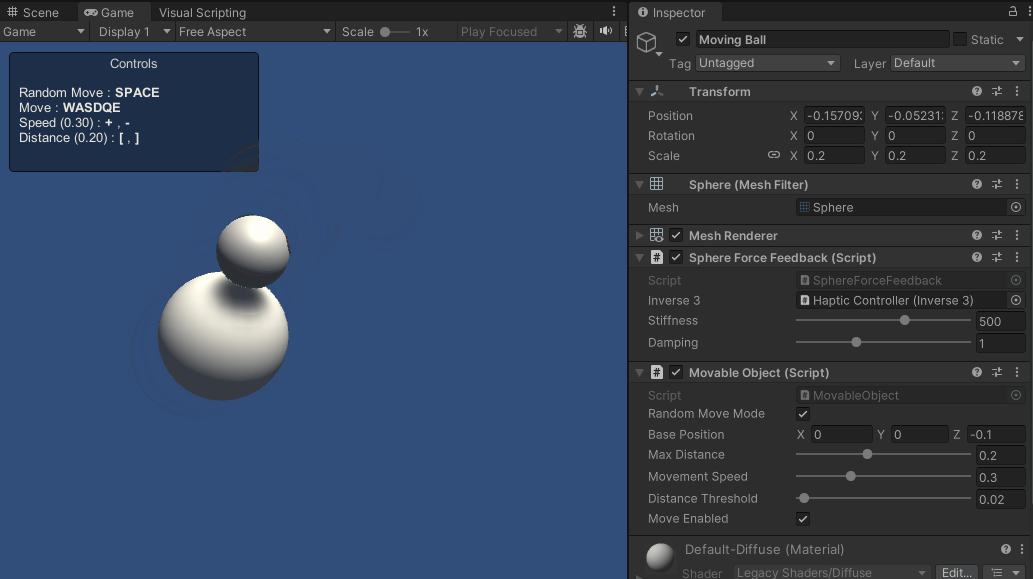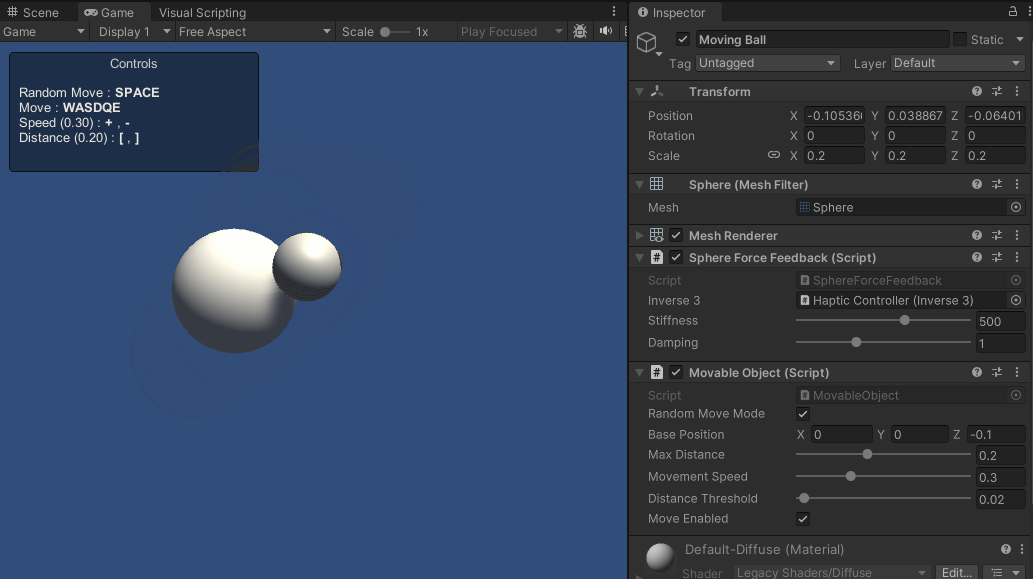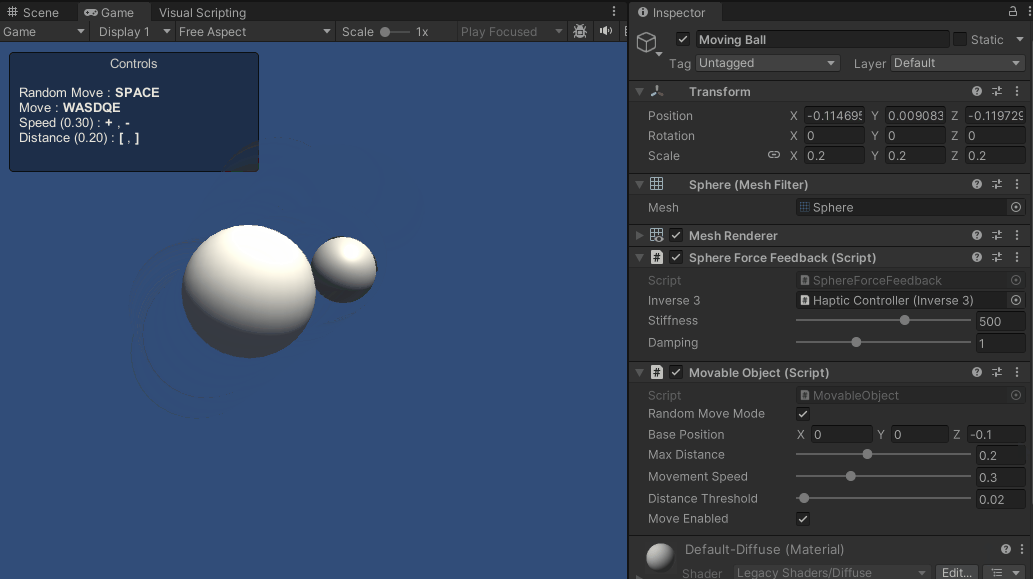
ソースファイル
この例の完全なシーンと関連ファイルは、Unity Package Manager のTutorialsサンプルからインポートできます。
について チュートリアル サンプルには
MovableObjectこのスクリプトは、複数の例で使用され、キーボード入力で付属のゲームオブジェクトの動きを制御します。
スフィアフォースフィードバック.cs
/*
* Copyright 2024 Haply Robotics Inc. All rights reserved.
*/
using System.Threading;
using Haply.Inverse.Unity;
using Haply.Samples.Tutorials.Utils;
using UnityEngine;
namespace Haply.Samples.Tutorials._4A_DynamicForceFeedback
{
public class SphereForceFeedback : MonoBehaviour
{
// must assign in inspector
public Inverse3 inverse3;
[Range(0, 800)]
// Stiffness of the force feedback.
public float stiffness = 300f;
[Range(0, 3)]
public float damping = 1f;
#region Thread-safe cached data
/// <summary>
/// Represents scene data that can be updated in the Update() call.
/// </summary>
private struct SceneData
{
public Vector3 ballPosition;
public Vector3 ballVelocity;
public float ballRadius;
public float cursorRadius;
}
/// <summary>
/// Cached version of the scene data.
/// </summary>
private SceneData _cachedSceneData;
private MovableObject _movableObject;
/// <summary>
/// Lock to ensure thread safety when reading or writing to the cache.
/// </summary>
private readonly ReaderWriterLockSlim _cacheLock = new();
/// <summary>
/// Safely reads the cached data.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>The cached scene data.</returns>
private SceneData GetSceneData()
{
_cacheLock.EnterReadLock();
try
{
return _cachedSceneData;
}
finally
{
_cacheLock.ExitReadLock();
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Safely updates the cached data.
/// </summary>
private void SaveSceneData()
{
_cacheLock.EnterWriteLock();
try
{
var t = transform;
_cachedSceneData.ballPosition = t.position;
_cachedSceneData.ballRadius = t.lossyScale.x / 2f;
_cachedSceneData.cursorRadius = inverse3.Cursor.Model.transform.lossyScale.x / 2f;
_cachedSceneData.ballVelocity = _movableObject.CursorVelocity;
}
finally
{
_cacheLock.ExitWriteLock();
}
}
#endregion
/// <summary>
/// Saves the initial scene data cache.
/// </summary>
private void Start()
{
_movableObject = GetComponent<MovableObject>();
SaveSceneData();
}
/// <summary>
/// Update scene data cache.
/// </summary>
private void FixedUpdate()
{
SaveSceneData();
}
/// <summary>
/// Subscribes to the DeviceStateChanged event.
/// </summary>
private void OnEnable()
{
inverse3.DeviceStateChanged += OnDeviceStateChanged;
}
/// <summary>
/// Unsubscribes from the DeviceStateChanged event.
/// </summary>
private void OnDisable()
{
inverse3.DeviceStateChanged -= OnDeviceStateChanged;
}
/// <summary>
/// Calculates the force based on the cursor's position and another sphere position.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="cursorPosition">The position of the cursor.</param>
/// <param name="cursorVelocity">The velocity of the cursor.</param>
/// <param name="cursorRadius">The radius of the cursor.</param>
/// <param name="otherPosition">The position of the other sphere (e.g., ball).</param>
/// <param name="otherVelocity">The velocity of the other sphere (e.g., ball).</param>
/// <param name="otherRadius">The radius of the other sphere.</param>
/// <returns>The calculated force vector.</returns>
private Vector3 ForceCalculation(Vector3 cursorPosition, Vector3 cursorVelocity, float cursorRadius,
Vector3 otherPosition, Vector3 otherVelocity, float otherRadius)
{
var force = Vector3.zero;
var distanceVector = cursorPosition - otherPosition;
var distance = distanceVector.magnitude;
var penetration = otherRadius + cursorRadius - distance;
if (penetration > 0)
{
// Normalize the distance vector to get the direction of the force
var normal = distanceVector.normalized;
// Calculate the force based on penetration
force = normal * penetration * stiffness;
// Calculate the relative velocity
var relativeVelocity = cursorVelocity - otherVelocity;
// Apply damping based on the relative velocity
force -= relativeVelocity * damping;
}
return force;
}
/// <summary>
/// Event handler that calculates and send the force to the device when the cursor's position changes.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="device">The Inverse3 device instance.</param>
private void OnDeviceStateChanged(Inverse3 device)
{
var sceneData = GetSceneData();
// Calculate the moving ball force.
var force = ForceCalculation(device.CursorLocalPosition, device.CursorLocalVelocity, sceneData.cursorRadius,
sceneData.ballPosition, sceneData.ballVelocity, sceneData.ballRadius);
// Apply the force to the cursor.
device.CursorSetLocalForce(force);
}
}
}